Answer: high pressures
The Ideal Gas equation is:
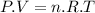
Where:
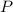 is the pressure of the gas
is the pressure of the gas
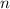 the number of moles of gas
the number of moles of gas
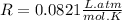 is the gas constant
is the gas constant
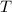 is the absolute temperature of the gas in Kelvin.
is the absolute temperature of the gas in Kelvin.
According to this law, molecules in gaseous state do not exert any force among them (attraction or repulsion) and the volume of these molecules is small, therefore negligible in comparison with the volume of the container that contains them.
Now, real gases can behave approximately to an ideal gas, under the conditions described above.
However, when temperature is low these gases deviate from the ideal gas behavior, because the molecules move slowly, allowing the repulsion or attraction forces to take effect.
The same happens at high pressures, because the volume of molecules is no longer negligible.