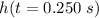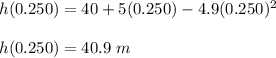Answer:
First option
The position of the sandbag at 0.250 s after its release is 40.9 m
Step-by-step explanation:
We want to know the height of the balloon as a function of time, after 0.250s
Then we use the following equation of motion:
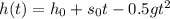
In this equation
 is the speed
is the speed
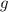 is gravitational acceleration
is gravitational acceleration
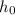 is the initial height
is the initial height
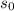 is the initial velocity.
is the initial velocity.
If the sandbag is released 40 meters above the ground, then the initial height is 40 meters.
As the balloon rises at a constant speed, then the initial velocity of the balloon is 5 m/s
Now we substitute these values in the formula
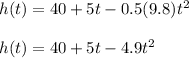
Now we look for: