Answer:
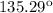
The figure attached will be helpful to understand the solution.
Here we see two cases, reflection and refraction of light.
According to the laws of reflection:
1. The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal are in the same plane.
2. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
*Note the normal is perpendicular to the plane, with a
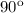 angle with the surface
angle with the surface
And this can be visualized in the figure, where the angle
 with which the incident ray hits the surface is equal to the angle with which this same ray is reflected.
with which the incident ray hits the surface is equal to the angle with which this same ray is reflected.
On the other hand we have Refraction, a phenomenon in which the light bends or changes its direction when passing through a medium with a refractive index different from the other medium.
In this context, the Refractive index is a number that describes how fast light propagates through a medium or material.
According to Snell’s Law:
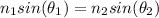 (1)
(1)
Where:
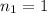 is the first medium refractive index (the air)
is the first medium refractive index (the air)
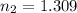 is the second medium refractive index (the ice)
is the second medium refractive index (the ice)
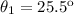 is the angle of the incident ray
is the angle of the incident ray
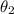 is the angle of the refracted ray
is the angle of the refracted ray
Now, firstly we have to find
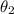 and then, by geometry, find
and then, by geometry, find
 and
and
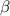 which sum the angle between the reflected and the refracted light.
which sum the angle between the reflected and the refracted light.
Finding
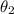 from (1):
from (1):
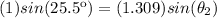
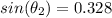
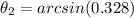
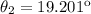 (2)
(2)
Remembering that the Normal makes a
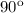 angle with the surface, we can say:
angle with the surface, we can say:
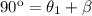 (3)
(3)
Finding
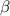 :
:
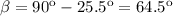 (4)
(4)
Doing the same with
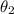 and
and
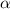 :
:
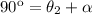 (5)
(5)
Finding
 :
:
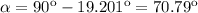 (6)
(6)
Adding both angles (4) and (6):
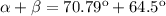 (7)
(7)
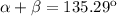 >>>This is the angle between the reflected and the refracted light.
>>>This is the angle between the reflected and the refracted light.