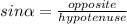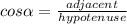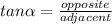Answer:
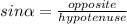
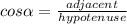
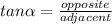
Explanation:
By definition, a right triangle is a triangle that has an angle of 90 degrees.
The basic trigonometric ratios are: sine, cosine and tangent.
Then, in a right triangle you can find the sine, the cosine or tangent of either of the non-90 degrees angles.
Given the right triangle shown in the image, you can find sine, cosine or tangent of the angle
 as following:
as following: