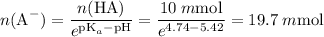20 mmol.
Step-by-step explanation
Let
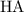 denotes acetic acid and
denotes acetic acid and
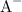 acetate ions. Apply the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation:
acetate ions. Apply the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation:
![\text{pH} = \text{pK}_a - \log{\frac{[\text{HA}]}{[\text{A}^(-)]}}](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/gjvh7wtlcyoao9qjqed9xa7w9ol6mllf2o.png) ,
,
where
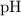 the intended pH of the buffer,
the intended pH of the buffer,
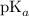 the pKa constant of the acetic acid, and
the pKa constant of the acetic acid, and
![\frac{[\text{HA}]}{[\text{A}^(-)]}](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/9629xpt3n6hq6qlh2ui8y7epru6hdcahk7.png) the ratio between the acetic acid and acetate ion concentrations in the solution.
the ratio between the acetic acid and acetate ion concentrations in the solution.
![\text{pH} = \text{pK}_a - \log{\frac{[\text{HA}]}{[\text{A}^(-)]}}\\\log{\frac{[\text{HA}]}{[\text{A}^(-)]}} = \text{pK}_a - \text{pH}\\\frac{[\text{HA}]}{[\text{A}^(-)]} = e^{\text{pK}_a -\text{pH}}](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/qogno5eq7bu7kl4r114ge9ve9pvd4yp77c.png) .
.
Volume is constant.
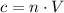 . As a result,
. As a result,
![\frac{n(\text{HA})}{n(\text{A}^(-))} = \frac{V\cdot[\text{HA}]}{V\cdot[\text{A}^(-)]} = \frac{[\text{HA}]}{[\text{A}^(-)]}=e^{\text{pK}_a-\text{pH}}](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/z5ymr4mmbdfingv7wil0slw3rl9yehjhxy.png) .
.