Potassium oxide: K₂O.
There's no need for prefixes since K₂O is an ionic compound.
Step-by-step explanation
Find the two elements on a periodic table:
- Potassium- K- on the left end of period four.
- Oxygen- O- near the right end of periodic two.
Elements on the bottom-left corner of the periodic table are metals. Those on the top-right corner are nonmetals.
- Potassium is a metal,
- Oxygen is a nonmetal.
A metal and a nonmetal combine to form an ionic compound. Potassium oxide is likely to be an ionic compound. It contains two types of ions:
- Potassium ions: Potassium is group 1 of the periodic table. It is an alkaline metal. Like other alkaline metals such as sodium Na, potassium K tends to lose one electron and form ions of charge +1 in compounds. The ion would be K⁺.
- Oxide ions from oxygen: Oxygen is the second most electronegative element on the periodic table. It tends to gain two electrons and form the oxide ion
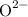 when it combines with metals.
when it combines with metals.
The two types of ions carry opposite charges. They shall pair up at a certain ratio such that they balance the charge on each other. The charge on each
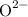 ion is twice that on a
ion is twice that on a
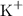 ion. Each
ion. Each
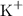 would pair up with two
would pair up with two
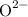 . Hence the subscript in the formula:
. Hence the subscript in the formula:
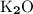 .
.
There are two classes of compounds:
- Covalent compounds, which need prefixes, and
- Ionic compounds, which need no prefix.
Prefixes are needed only in covalent compounds. For instance in the covalent compound carbon dioxide
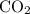 , the prefix di- indicates that there are two oxygen atoms in the formula
, the prefix di- indicates that there are two oxygen atoms in the formula
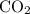 . However, there's no need for prefix in ionic compounds such as
. However, there's no need for prefix in ionic compounds such as
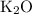 .
.