Similarities:
- The gravitational force and the electric force have a similar form.
In fact, gravitational force is given by:
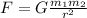
where G is the gravitational constant, m1 and m2 are the masses of the two objects, r is the separation between the two objects.
The electric force is given by:
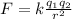
where k is the Coulomb constant, q1 and q2 are the charges of the two objects, r is the separation between the two objects.
As we see, the two forces have same dependency on the distance (inversely proportional to the square of the distance)
- Both forces are non-contact forces: this means that in both cases, the two objects do not to be in contact with each other, because the force is still acting from a distance also.
Differencies:
- The gravitational force is attractive only; on the contrary, the electric force can be either attractive or repulsive, depending on the relative sign of the two charges. In fact, when the two charges have same sign, the force is repulsive; when the two charges have opposite sign, the force is attractive.
- The gravitational force is much weaker than the electric force. This can be seen by comparing the value of the constant in the two formulas; we have:
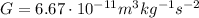 for the gravitational force
for the gravitational force
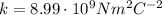 for the electric force
for the electric force
As we see, the electric force is much stronger than the gravitational force.