Answer:
1) The half-reaction that occurs at the anode is :
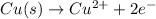
2)+0.60 V is the E° for the spontaneous reaction.
Step-by-step explanation:
1)
Oxidation reaction is defined as the reaction in which an atom looses its electrons.
Reduction reaction is defined as the reaction in which an atom gains electrons. Here, the oxidation state of the atom decreases.
Oxidation reaction occurs at anode.
Oxidation half reaction:
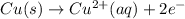
Reduction reaction occurs at cathode.
Reduction half reaction:
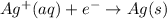
Net reaction:
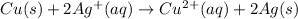
2)
Reduction potential of nickel(II) ions to nickel =
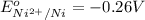
Reduction potential of copper (II) ions to copper =
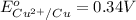
To calculate the
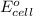 of the reaction, we use the equation:
of the reaction, we use the equation:
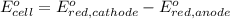
Substance with higher or positive reduction potential goes on cathode and substance with lower of more negative reduction potential goes on anode.
Putting values in above equation, we get:
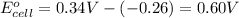
+0.60 V is the E° for the spontaneous reaction.