Answer:
it will increase the amount of carbon monoxide hence will increase the partial pressure of CO.
Step-by-step explanation:
The reaction is:
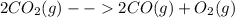 ∆H° = -514
∆H° = -514
The reaction is
a) Exothermic
b) There are more gaseous moles on product side
c) carbon dioxide is the reactant and carbon monoxide and oxygen are products.
According to Le-Chatelier's Principle if we bring any change in the equilibrium reaction, the equilibrium shifts in the direction where it can nullify the change.
i) If we remove oxygen (product) then the reaction will shift in the forward direction.
It means it will increase the amount of carbon monoxide hence will increase the partial pressure of CO.
There will be no effect on the equilibrium constant.
The partial pressure of carbon dioxide will decrease.