Answer: Option (b) is the correct answer.
Step-by-step explanation:
According to ideal gas law, the product of pressure and volume is equal to the product of number of moles, gas constant and temperature.
Mathematically, PV = nRT
So, when there are two gases with equal number of moles behaving ideally then the ideal gas equation will be as follows.
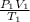 =
=
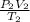
and
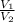 =
=
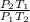
Hence, when temperature and pressure of both the gases will be constant then
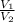 = 1.
= 1.
Thus, we can conclude that constant temperature and pressure is the conditions that must be met for a volume ratio to be created from a balanced chemical equation.