Answer:
The value of k is
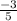
The roots are -1 and
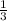
Explanation:
In any quadratic equation
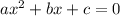 the sum of its roots is
the sum of its roots is
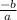 and the product of its root is
and the product of its root is
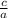
In the equation
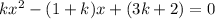
The sum is

The product is
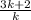
∵ The sum of the roots is twice their product
∴
![(k+1)/(k)=2[(3k+2)/(k)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/ihdybvltt28px0m85fmkwzmw5py5mmptzz.png)
∴
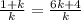 ⇒Multiply both sides by k
⇒Multiply both sides by k
1 + k = 6k + 4⇒ 1 - 4 = 6k - k
5k = -3 ⇒
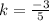
Use the value of k in the equation:
![(-3)/(5)x^(2)-[1+(-3)/(5)]x+[(3)((-3)/(5))+2]=0](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/706gn2fjk2elx8m43m94bw6wq5rbdfb0e5.png)
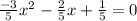 ⇒ Multiply equation by 5
⇒ Multiply equation by 5
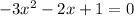 ⇒ Multiply equation by -1
⇒ Multiply equation by -1
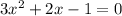 ⇒ use factorization to find roots
⇒ use factorization to find roots
(3x - 1)(x + 1) = 0
3x -1 = 0⇒ 3x = 1⇒ x = 1/3
x + 1 = 0⇒ x = -1
The roots are 1/3 and -1