Answer: 690 s
Explanation: Rate law says that rate of a reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactants each raised to a stoichiometric coefficient determined experimentally called as order.
For a reaction:
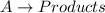
![Rate=k[A]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/thpzkh7xg8m8henb76km4wayj6uzunmh80.png)
k= rate constant=
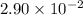
x = 2= order with respect to A
For a second order reaction,
![t_(1)/(2)=(1)/(k* [A_0])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/wlad9q9fmgq1uxmymj9h1em1slikdf3jiu.png)
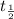 = half life = time taken for a reaction to complete to half.
= half life = time taken for a reaction to complete to half.
![[A_0]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/izynxfnwyud2ghdog9l8ny0mhzwshbud6r.png) =initial concentration= 0.0500 M
=initial concentration= 0.0500 M
Thus
![t_{(1)/(2)=(1)/(2.90* 10^(-2)* [0.0500])=690s](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/fj6uqu1bim17p9nkb44h5hhk0lwg9zd5qm.png)