Answer:
For 1: The number of moles of the gas is 0.056 moles.
For 2: The new volume of the gas is 931.74 mL.
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles of gas, we use the equation given by ideal gas, which is:
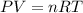
where,
P = pressure of the gas = 750 torr
V = volume of the gas = 1.35 L
n = Number of moles of gas = ? mol
R = Gas constant =
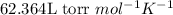
T = temperature of the gas = 17°C = 290 K (Conversion factor:
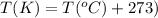
Putting values in above equation, we get:
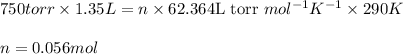
Hence, the number of moles of the gas is 0.056 mol.
Here, the number of moles of the gas remains the same all the other variables are changing.
To calculate the new volume of the gas, we use the equation given by ideal gas, which is:
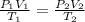
where,
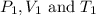 are initial pressure, volume and temperature of the gas
are initial pressure, volume and temperature of the gas
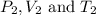 are final pressure, volume and temperature of the gas
are final pressure, volume and temperature of the gas
We are given:

Putting values in above equation, we get:
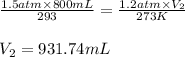
Hence, the final volume of the gas will be 931.74 mL.