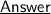
An equation is called any equality that contains one or more unknown quantities, which are called unknowns, and that are only generally verified for certain values of the unknowns.
Thus, for example: 4x - 2 = 3x + 1~4x−2=3x+1 is an equation because it is an equality in which there is one unknown, xx .
⇝Equation resolution:
![\qquad \sf \dashrightarrow4x - 2 = 3x + 14x−2=3x+1</strong></p><p><strong>[tex] \qquad \sf \dashrightarrow4x - 2 = 3x + 14x−2=3x+1](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/r62quhqmy4lymzzl0h5t.png)
We transpose the term 3x to the first member.
3x to the first member.We will have:
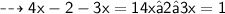
Next we transpose the term -2 to the second member.
We will have:
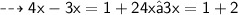
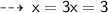
Let's check that x = 3x=3 satisfies the given equation:
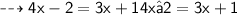
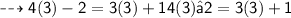
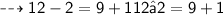
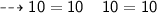
That is, 10 = 10, as we wanted to verify.
I hope I've helped : )