Answer:
3n² + 5n - 2
Explanation:
Given sequence:
6, 20, 40, 66, 98, 136, ...
Calculate the first differences between the terms:
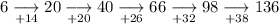
As the first differences are not the same, calculate the second differences:
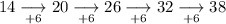
As the second differences are the same, the sequence is quadratic and will contain an n² term.
The coefficient of the n² term is half of the second difference.
Therefore, the n² term is: 3n²
Compare 3n² with the given sequence:
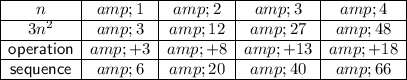
The second operations are different, therefore calculate the differences between the second operations:
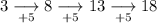
As the differences are the same, we need to add 5n as the second operation:

Finally, we can clearly see that the operation to get from 3n² + 5n to the given sequence is to subtract 2.
Therefore, the nth term of the quadratic sequence is:
3n² + 5n - 2