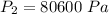Answer:
a
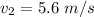
b
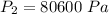
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The pressure of the water in the pipe is
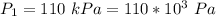
The speed of the water is
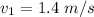
The original area of the pipe is
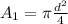
The new area of the pipe is
![A_2 = \pi * ([(d)/(2) ]^2)/(4) = \pi * ((d^2)/(4) )/(4) = \pi (d^2)/(16)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/high-school/e7ib1cdx434m5wxdc05pg4ott9wlpfbsfc.png)
Generally the continuity equation is mathematically represented as
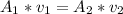
Here
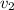 is the new velocity
is the new velocity
So
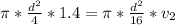
=>
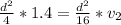
=>
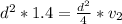
=>
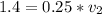
=>
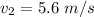
Generally given that the height of the original pipe and the narrower pipe are the same , then we will b making use of the Bernoulli's equation for constant height to calculate the pressure
This is mathematically represented as
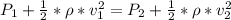
Here
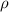 is the density of water with value
is the density of water with value
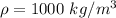
![P_2 = P_1 + (1)/(2) * \rho [ v_1^2 - v_2^2 ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/high-school/o4d4danvxml075h9toedgrom1pn1aqt21c.png)
=>
![P_2 = 110 *10^(3) + (1)/(2) * 1000 * [ 1.4 ^2 - 5.6 ^2 ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/high-school/rwnf9hoy9zambkoe76835rjzihw2g9o6b2.png)
=>