Complete Question
Calculate the equilibrium amounts of each substance in the reaction below if an initial amount of 0.400 moles of CO are brought together with an initial amount of 2.20 moles of Cl2 in a 1.00 L vessel and then equilibrium is established at 900 K. Kc at this temperature = 0.800. COCl2(g) CO(g) + Cl2(g)
Answer:
The amount of each substance at equilibrium is
![[COCl_2 ] = 0.282 \ M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/c9klyaguf05de5t6udvku6hyeab6c47cp2.png)
![[CO] = 0.12 \ M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/49zp4hwx3jsodvy9yu2rzuq1n90egld827.png)
![[Cl_2] = 2.008 \ M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/rfmac70cmaqn3iudfe8r41x7ezr6uami83.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The initial amount of CO is
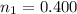
The initial amount of
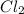 is
is
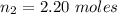
The volume of the vessel is
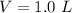
The temperature is
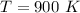
The equilibrium constant at the given temperature is
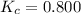
The reaction is
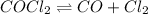
Now Generating an I C E table
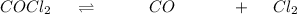
Initial [I] 0 0.400 2.20
Change [C ] + x -x - x
Equilibrium [E ] x 0.400- x 2.20 - x
Here x is the amount in terms of concentration by which
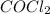 and
and
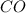 and
and
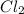 decreased during the reaction
decreased during the reaction
Generally the equilibrium constant is mathematically represented as
![K_c = ([CO] [Cl_2])/([COCl_2])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/ydu9joramieb97nb9zfgyriiw8d1zux010.png)
=>
![0.800 = ([0.400 - x] [2.20 - x ])/([x])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/l4lrpz78uaoeiivwflttjdkktw3k9kej9j.png)
=>
![0.800 x = [0.400 - x ] * [ 2.20 - x ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/1v7mfb68qjyyivwezvxkpljra4h24wh7aw.png)
=>
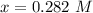
Generally at equilibrium the amount of
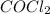 present is
present is
![[COCl_2 ] = 0.282 \ M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/c9klyaguf05de5t6udvku6hyeab6c47cp2.png)
Generally the equilibrium the amount of
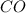 present is
present is
![[CO] = 0.400 - 0.282](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/gwi6qh28om9s7hqkiyzm14t3ee469a7mht.png)
=>
![[CO] = 0.12 \ M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/49zp4hwx3jsodvy9yu2rzuq1n90egld827.png)
Generally the equilibrium the amount of
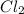 present is
present is
![[Cl_2 ] = 2.29 - 0.282](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/gqifydvmmcq64ezzsc1xw3vcjnbsh1a4pz.png)
=>
![[Cl_2] = 2.008 \ M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/rfmac70cmaqn3iudfe8r41x7ezr6uami83.png)