Answer: The amount of moles that can be produced when 156.1 grams of CuO are consumed is .653 moles.
Explanation: The first thing to do is to convert the 156.1 grams of Copper(II) Oxide (CuO).
In order to convert the 156.1 grams of Copper(II) Oxide to moles we have to first calculate the molar mass of Copper(II) Oxide. This can be done by simply adding the Copper's molar mass, 63.5, to the Oxygen's molar mass, 16.
16 g + 63.5 g = 79.5 g
Once you have obtained the molar mass of the Copper (II) Oxide you can then proceed to convert the 156.1 grams from before into moles.
This is done by multiplying 156.1 grams by 1 mole / 79.5 grams.
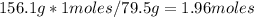
Now that you have calculated the 1.96 moles of Copper(II) Oxide, you need to set up an equation to convert between moles amounts.
This can be done by looking at the coefficients in the chemical equation. So, in this chemical reaction, it tells us for every 3 moles of CuO there is 1 moles of N2.
With this we can write a conversion equation as follows.
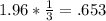
*Note: in conversion equations the denominator should match the units and or element being multiplied by the other fraction in the numerator. Such as in this instance the 1.96 moles of CuO and 3 moles of CuO are the same.
So, the amount of moles of N2 that can be made when 156.1 grams of CuO are consumed is .653 moles.