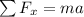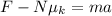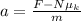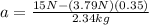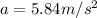Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
In order to solve this problem, we will need to draw a free body diagram of both situations (see attached picture).
So first, we need to find what the mass of the object is. We can do so by analyzing the horizontal movement of the first situation, so we get:
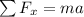
F=ma
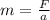
so
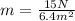
m=2.34kg
next, we can analyze the second situation, we will start by analizing the vertical movement so we can determine the Normal force, so we get:
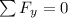
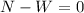
N=W
N=mg
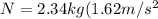
N=3.79N
so now we can analyze the horizontal movement of the block, so we get: