Answer:
A) P(Z > 5000) = 0.0322
B) P( Y = 2 or 3) ≅ 0.9032
Explanation:
From the given information;
Suppose the sales for the first week are denoted by X and the sales for the second week are denoted by Y.
Then;
X & Y are independent and they follow a normal distribution.
i.e.
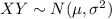
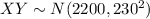
If we set Z to be equal to X+Y
Then,
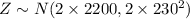 since two normal distribution appears normal
since two normal distribution appears normal
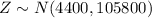
So;
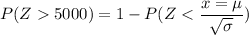
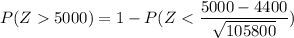
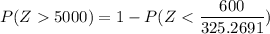
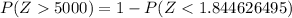
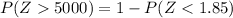
From the Z - tables;
P(Z > 5000) = 1 - 0.9678
P(Z > 5000) = 0.0322
B)
Let Y be the random variable that obeys the Binomial distribution.
Y represents the numbers of weeks in the next 3 weeks where the gross weekly sales exceed $2000
Thus;
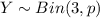
where;
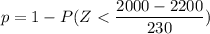
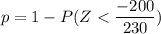
p = 1 - P( Z < - 0.869565)
From the Z - tables;
p = 1 - 0.1924
p = 0.8076
Now;
P(Y ≥ 2) = P(Y = 2) + P( Y =3 )
Using the formula
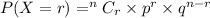
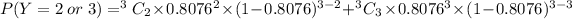
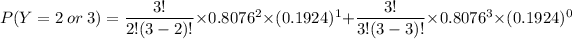
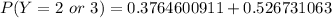
P( Y = 2 or 3) = 0.9031911541
P( Y = 2 or 3) ≅ 0.9032